Regularization
it basically adds the penalty as model complexity increases.
Regularization parameter(lambda) penalizes all the parameters except intercept so that model generalizes the data and won’t overfit.
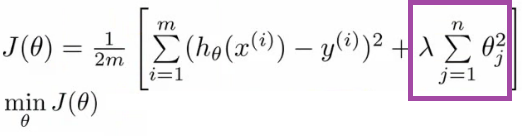
L1 Regularization
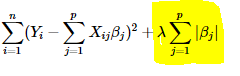
L2 regularization:
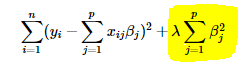
The key difference between these techniques is that Lasso shrinks the less important feature’s coefficient to zero thus, removing some feature altogether. So, this works well for feature selection in case we have a huge number of features.
SGD and Mini_batch
Contrasting the 3 Types of Gradient Descent
SGD:
Stochastic gradient descent,
upsides:
- the frequent updates immediately give an insight into the performance of the model and the rate of improvement.
- this variant of gradient descent may be the simplest to understand and implement, especially for beginners.
- increased model update frequency can result in faster learning on some problem
- noisy update can allow model to avoid local minima.
Downsides:
- update so frequently is more computationally expensive than other configurations.
- the frequent updates can result in noisy gradient signal, which may cause the model parameters and model error to jump around.
- noisy learning process down the error gradient can also make it hard for algorithm to settle.
Batch Gradient Descent
batch gradient descent performs model updates at the end of each training epoch.
Upsides:
- Fewer updates to the model means this variant of gradient descent is more computationally efficient.
- decreased update frequency results in a more stable error gradient and may result in a more stable convergence
- the separation of the calculation of prediction errors and the model update lends the algorithm to parallel processing based implementations. #### Downsides:
- more stable error gradient may result in premature convergence of the model to a less optimal set of parameters.
- the updates at the end of the training epoch require the additional complexity of accumulating prediction errors across all training examples.
- requires the entire training set in memory and available to the algorithm.
- model updates may be slow for large dataset.
## Mini-Batch gradient descent.
split training dataset into small batches that are used to calculate model error and update model coefficients.
upsides:
- more robust convergence, avoid local minima.
- batched updates provide a computationally more efficient process than stochastic gradient descent.
- batching allows both the efficientcy of not having all training data in memory and algorithm implementations.
downsides:
- mini-batch requires the configuration of an additional “mini-batch” hyperparameter.
Optimization
Gradient Descend:
for i in range(nb_epochs):
params_grad = evaluate_gradient(loss_function, data, params)
params = params - learning_rate * params_grad
Stochastic gradient descent(GSD)
for i in range(nb_epochs):
np.random.shuffle(data)
for example in data:
params_grad = evaluate_gradient(loss_function , example , params)
params = params - learning_rate * params_grad
Mini-Batch gradient descent
Usually when talk about SGD, we are refering to Mini-batch SGD
Improvement
1.1 Momentum
1.2 nesterov momentum
nesterov的好处就是,当梯度方向快要改变的时候,它提前获得了该信息,从而减弱了这个过程,再次减少了无用的迭代。
1.3 Adagrad
思路很简单,不同的参数是需要不同的学习率的,有的要慢慢学,有的要快快学,所以就给了一个权重咯,而且是用了历史上所有的梯度幅值。
1.4 Adadelta & Rmsprop
adagrad用了所有的梯度,问题也就来了,累加的梯度幅值是越来越大的。导致学习率前面的乘因子越来越小,后来就学不动了呀。
Adadelta就只是动了一丢丢小心思,用移动平均的方法计算累加梯度,只累加了一个窗口的梯度,而且计算方法也更有效。
<img src=’https://mmbiz.qpic.cn/mmbiz_jpg/AIR6eRePgjOrsxPM1PR6BFj7v0JTvq3TcetncLdGjhqLicsWLFyeOTclK5yImtOHJOdtibariblDT8nmOr4nIdFVg/640?wx_fmt=jpeg&tp=webp&wxfrom=5&wx_lazy=1&wx_co=1>
将学习率用前一时刻参数的平方根来代替,最终更新算法变成了这样。
Adam Optimization
moment:
- first moment: just the mean
- secodn momentL is usually just the variance
- raw moment: n-th raw moment = [x1^n+x2^n+….+xk^n]/k
- center moment: before rasing to a power, substract the mean.
- second central moment:[(x1-m)^2+(x2-m)^2+..]/k
- then first central moment of a set of numbers is always 0.
in machine learning, the term “first moment” often means the “first raw moment” (which is the mean) and the term “second moment” often means “the second central moment”,
最后就是这个adam算法,作为最晚出现的,当然是集大成者。
adam对梯度的一阶和二阶都进行了估计与偏差修正,使用梯度的一阶矩估计和二阶矩估计来动态调整每个参数的学习率。